Tel: +86 311 8595 5658 E-mail: admin@yuanlvfilter.com
Water intake systems play a vital role in hydropower, irrigation, and wastewater treatment. Yet one persistent challenge engineers face is screen clogging—a problem that can restrict flow, reduce efficiency, and increase maintenance costs. Understanding the root causes of clogging and how modern Coanda wedge wire screens overcome them is essential for improving long-term performance.
1. Sediment and Silt Accumulation
Rivers, reservoirs, and surface water sources carry fine particles such as sand, silt, and clay. Over time, these materials settle on the intake surface, forming compact layers that reduce open area and disrupt flow.
Result: Lower intake capacity, increased backpressure, and frequent manual cleaning.
2. Organic Matter and Debris
Leaves, twigs, aquatic plants, and trash can quickly block conventional mesh or perforated intake screens. Organic buildup is especially problematic in seasonal conditions when water flow carries more floating debris.
Result: Uneven flow distribution and potential pump cavitation.
3. Algae and Biofouling
In warm, nutrient-rich environments, algae and microorganisms attach to screen surfaces, creating biological films that restrict flow and trap additional debris.
Result: Progressive clogging that is difficult to remove without chemical cleaning or downtime.
4. Insufficient Flow Velocity
When intake velocity is too low, particles are not effectively swept away from the screen surface. Stagnant flow zones promote sedimentation and accelerate fouling.
Result: Increased maintenance intervals and reduced hydraulic efficiency.
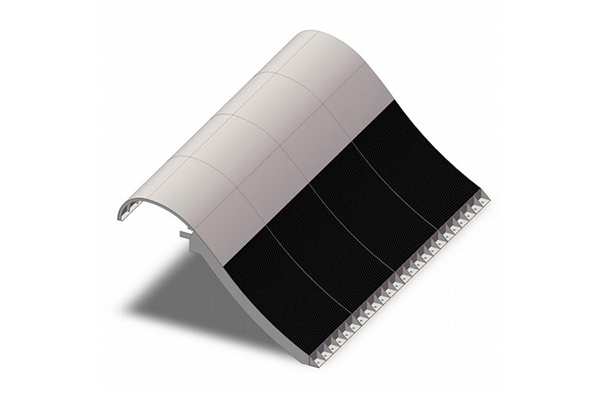
1. The Coanda Effect for Self-Cleaning Flow
The Coanda screen uses a curved wedge wire profile that harnesses gravity and surface tension to direct water along the screen face. The thin layer of flow, called the Coanda effect, deflects solids away from the intake while allowing clean water to pass through.
Benefit: Continuous self-cleaning without mechanical brushes or backwash systems.
2. Precision Wedge Wire Design
Each screen is manufactured with triangular V-shaped wire profiles and precisely controlled slot openings. This structure provides a large open area while preventing fine particles from entering the system.
Benefit: High efficiency and low head loss, even under variable flow conditions.
3. Reduced Maintenance and Downtime
Because the Coanda wedge wire screen resists clogging naturally, operators spend less time on cleaning and replacement. The self-cleaning hydraulic action minimizes manual intervention.
Benefit: Lower operating costs and increased system reliability.
4. Durable Stainless Steel Construction
Made from corrosion-resistant stainless steel, Coanda screens can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including abrasive particles and fluctuating water chemistry.
Benefit: Long service life and stable performance in both freshwater and seawater applications.
Continuous, maintenance-free operation
Efficient debris exclusion and sediment control
Stable hydraulic performance with minimal head loss
Environmentally friendly and fish-safe design
Customizable slot sizes and configurations
Applications
Coanda wedge wire intake screens are ideal for:
Hydropower plants
Surface water and river intakes
Irrigation and drainage systems
Desalination pretreatment
Industrial process water filtration
Clogging on intake screens is a costly and time-consuming issue, but it doesn't have to be. The Coanda wedge wire screen offers an innovative solution that leverages physics, precision engineering, and durable materials to keep water flowing freely. By choosing a self-cleaning, low-maintenance Coanda intake design, operators can ensure higher efficiency, reduced downtime, and long-term cost savings.
1. What materials are Coanda screens made from?
Most Coanda wedge wire screens are built from stainless steel (304 or 316L), ensuring corrosion resistance, high strength, and a long service life even in harsh water environments.
2. Are Coanda wedge wire screens suitable for all water types?
Yes. They perform efficiently in river water, surface water, seawater, and wastewater applications, maintaining stable performance under varying flow and sediment conditions.
3. How often do Coanda intake screens need maintenance?
Because of their self-cleaning design, Coanda screens require minimal manual cleaning. Routine inspection is recommended, but frequent maintenance or backflushing is usually unnecessary.